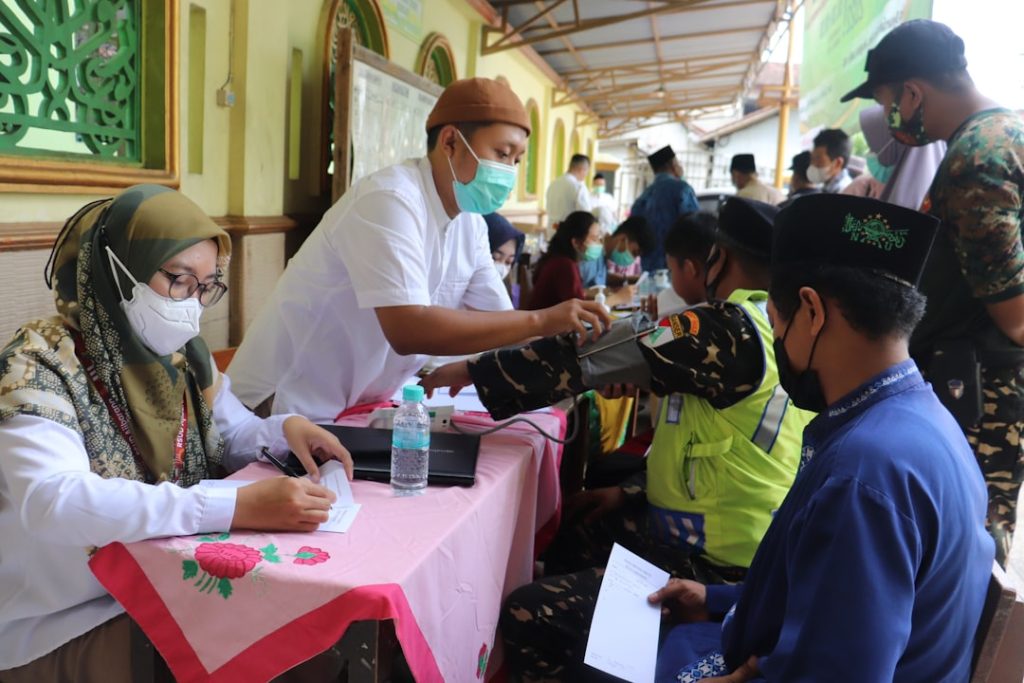
Medical trial volunteers serve as the backbone of clinical research, providing the essential data that drives medical advancements. These individuals participate in trials designed to test new drugs, therapies, and medical devices, often before they are made available to the general public. By volunteering, they contribute to a body of knowledge that can lead to breakthroughs in treatment and prevention strategies for various diseases.
For instance, the rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines was made possible largely due to the willingness of thousands of volunteers who participated in clinical trials. Their contributions allowed researchers to assess the safety and efficacy of these vaccines in real-time, ultimately leading to widespread immunization efforts that have saved countless lives. Moreover, medical trial volunteers help researchers understand how different populations respond to treatments.
This is crucial because the effectiveness of a drug can vary significantly based on genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. For example, a medication that works well in one demographic may not have the same effect in another due to variations in metabolism or disease prevalence. By including a diverse group of volunteers, researchers can gather comprehensive data that reflects the broader population, ensuring that new treatments are safe and effective for everyone.
This aspect of volunteerism not only accelerates the pace of medical innovation but also enhances the quality of care that patients receive once new therapies are approved.
Key Takeaways
- Medical trial volunteers are essential for developing new treatments and advancing medical knowledge.
- Diverse participation in trials ensures treatments are effective and safe for all populations.
- Ethical standards protect volunteers and maintain the integrity of medical research.
- Volunteers often make personal sacrifices to contribute to public health improvements.
- Supporting and recognizing volunteers encourages ongoing participation and advances future medical breakthroughs.
The Impact of Medical Trials on Public Health
The implications of medical trials extend far beyond individual participants; they have a profound impact on public health as a whole. Clinical trials are essential for determining the safety and efficacy of new treatments before they reach the market. This process is critical for preventing harmful side effects and ensuring that new medications provide real benefits to patients.
For instance, the development of antiretroviral therapy for HIV/AIDS was significantly advanced through clinical trials that tested various drug combinations. These trials not only improved treatment options but also transformed HIV from a fatal disease into a manageable chronic condition for many individuals. Furthermore, medical trials can lead to significant public health initiatives aimed at disease prevention.
For example, large-scale trials investigating vaccines have historically played a pivotal role in controlling infectious diseases. The eradication of smallpox and the significant reduction in polio cases worldwide can be attributed to rigorous vaccine trials that established their safety and effectiveness. As new pathogens emerge and existing diseases evolve, ongoing clinical research remains vital for developing vaccines and treatments that protect public health on a global scale.
The Importance of Diversity in Medical Trial Volunteers
Diversity among medical trial volunteers is not merely a matter of representation; it is essential for the validity and applicability of research findings. Historically, clinical trials have often underrepresented certain demographic groups, including racial and ethnic minorities, women, and older adults. This lack of diversity can lead to skewed results that do not accurately reflect how different populations respond to treatments.
For example, many medications have been found to have different side effects or levels of efficacy based on genetic variations prevalent in specific ethnic groups. By ensuring that clinical trials include a diverse array of participants, researchers can better understand these differences and develop treatments that are effective for all. Moreover, diverse participation in clinical trials fosters trust between communities and the medical research establishment.
Marginalized groups may be hesitant to participate in research due to historical injustices or mistrust stemming from unethical practices in the past. By actively recruiting diverse volunteers and ensuring their voices are heard throughout the research process, the medical community can work towards rebuilding this trust. Initiatives aimed at increasing diversity not only enhance the quality of research but also promote health equity by ensuring that all populations benefit from medical advancements.
The Ethical Considerations of Medical Trials
The ethical landscape surrounding medical trials is complex and multifaceted. One of the primary ethical considerations is informed consent, which requires that participants fully understand the nature of the trial, including potential risks and benefits, before agreeing to participate. Researchers must ensure that volunteers are not coerced into participation and that they have the autonomy to withdraw from the study at any time without penalty.
This principle is foundational to ethical research practices and is designed to protect the rights and well-being of participants. Additionally, ethical considerations extend to the design and conduct of trials themselves. Researchers must balance the need for rigorous scientific inquiry with the obligation to minimize harm to participants.
This includes conducting thorough risk assessments and implementing safeguards to protect volunteers from adverse effects. The establishment of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) plays a crucial role in this process by reviewing trial protocols to ensure they meet ethical standards before they can proceed. These boards help maintain public trust in medical research by ensuring that ethical guidelines are upheld throughout the trial process.
The Personal Sacrifices of Medical Trial Volunteers
| Metric | Description | Example Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Volunteers Enrolled | Number of participants registered for the trial | 250 | Individuals |
| Age Range | Minimum and maximum age of volunteers | 18 – 65 | Years |
| Gender Distribution | Percentage of male and female volunteers | Male: 48%, Female: 52% | Percentage |
| Dropout Rate | Percentage of volunteers who left the trial before completion | 7% | Percentage |
| Adverse Events Reported | Number of volunteers reporting side effects or complications | 15 | Individuals |
| Average Duration of Participation | Mean length of time volunteers stayed in the trial | 12 | Weeks |
| Compliance Rate | Percentage of volunteers following the trial protocol correctly | 95% | Percentage |
Volunteering for medical trials often involves personal sacrifices that can impact participants’ lives in various ways. Many volunteers face uncertainties regarding their health as they may be exposed to experimental treatments with unknown side effects. While some may experience positive outcomes, others might endure adverse reactions or complications that could affect their quality of life.
For instance, individuals participating in trials for cancer treatments may undergo rigorous testing and experience significant physical and emotional challenges as they navigate their participation. Moreover, the time commitment required for participation can be substantial. Volunteers may need to attend multiple appointments for screenings, treatments, and follow-up evaluations, which can disrupt their daily lives and responsibilities.
This commitment can be particularly challenging for those with jobs or family obligations. Despite these sacrifices, many volunteers are motivated by a desire to contribute to scientific knowledge and help others facing similar health challenges. Their willingness to endure discomfort or uncertainty underscores the altruistic nature of volunteerism in medical research.
The Future of Medicine and the Role of Volunteerism

As medicine continues to evolve with advancements in technology and personalized medicine, the role of volunteerism in clinical trials will become increasingly vital. The rise of precision medicine—tailoring treatments based on individual genetic profiles—relies heavily on diverse volunteer participation in clinical studies. As researchers seek to understand how genetic variations influence treatment responses, a broad base of volunteers will be essential for generating meaningful data.
Additionally, emerging technologies such as telemedicine and digital health tools are transforming how clinical trials are conducted. Remote monitoring and virtual participation options can make it easier for individuals to engage in research without the burden of travel or time constraints. This shift could lead to increased participation rates among diverse populations who may have previously faced barriers to involvement.
As these innovations continue to develop, volunteerism will remain a cornerstone of advancing medical knowledge and improving patient care.
Recognizing and Supporting Medical Trial Volunteers
Recognizing the contributions of medical trial volunteers is crucial for fostering a culture of appreciation within the research community. Many organizations are beginning to implement programs aimed at acknowledging volunteers’ efforts through awards, recognition events, or even financial compensation for their time and commitment. Such initiatives not only honor individual contributions but also raise awareness about the importance of volunteerism in advancing medical science.
Support systems for volunteers are equally important. Providing resources such as counseling services or peer support groups can help participants navigate the emotional challenges associated with trial participation. Additionally, clear communication about trial processes and expectations can empower volunteers by ensuring they feel informed and valued throughout their journey.
By creating an environment that prioritizes volunteer well-being, researchers can enhance recruitment efforts and encourage more individuals to consider participating in clinical trials.
How to Get Involved as a Medical Trial Volunteer
For those interested in becoming medical trial volunteers, several avenues exist for getting involved in this impactful form of service. One effective way is to consult with healthcare providers who can offer guidance on ongoing clinical trials relevant to specific health conditions or interests. Many hospitals and research institutions maintain databases listing current studies seeking participants, making it easier for individuals to find opportunities that align with their circumstances.
Additionally, online platforms dedicated to clinical trial recruitment have emerged as valuable resources for potential volunteers. Websites such as ClinicalTrials.gov provide comprehensive listings of studies across various fields, allowing users to search by location, condition, or treatment type. These platforms often include detailed information about trial protocols, eligibility criteria, and contact information for researchers overseeing each study.
Engaging with local advocacy groups or patient organizations can also provide insights into upcoming trials while fostering connections with others who share similar health concerns or interests in research participation. Ultimately, becoming a medical trial volunteer is not only an opportunity to contribute to scientific progress but also a chance to be part of a community dedicated to improving health outcomes for future generations.




