Electronic Data Capture (EDC) software has evolved into a fundamental tool for modern clinical research. Its implementation aims to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and overall management of clinical trials. This article explores how EDC software contributes to streamlining these complex processes.
Understanding Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Software
EDC software replaces traditional paper-based case report forms (CRFs) with digital alternatives. This shift provides a centralized platform for collecting, storing, and managing data generated during clinical trials. Think of it as moving from a filing cabinet overflowing with paper documents to a secure, organized digital library. The primary goal is to capture data at its source, minimizing transcription errors inherent in manual processes.
Key Features of EDC Solutions
Modern EDC systems offer a spectrum of functionalities designed to enhance data collection. These often include:
Real-time Data Entry and Validation
Real-time data entry allows study staff to input information as soon as it is collected. This immediate capture reduces the lag between patient visit and data availability. Integrated validation checks, often referred to as edit checks, are crucial. These are programmed rules that verify the plausibility and consistency of entered data, flagging potential errors or discrepancies before they become deeply embedded in the dataset. For instance, if a lab value falls outside a predetermined normal range, the system can immediately prompt the user for clarification or correction. This proactive approach is like a vigilant gatekeeper, ensuring only valid information proceeds.
Customizable Electronic Case Report Forms (eCRFs)
EDC software enables the creation of digital eCRFs that mirror the design and content of traditional paper CRFs. The customization aspect is vital, allowing researchers to tailor forms to the specific requirements of their study protocol, including various question types, skip logic, and branching. This flexibility means the software adapts to the trial, not the other way around.
Data Management and Monitoring Capabilities
Beyond mere data entry, EDC systems provide robust tools for data management. This includes features for query management, where data discrepancies are identified and resolved collaboratively between site staff and data managers. Integrated monitoring dashboards offer real-time visibility into study progress and data quality, acting as a command center for oversight.
The Impact of EDC on Trial Efficiency
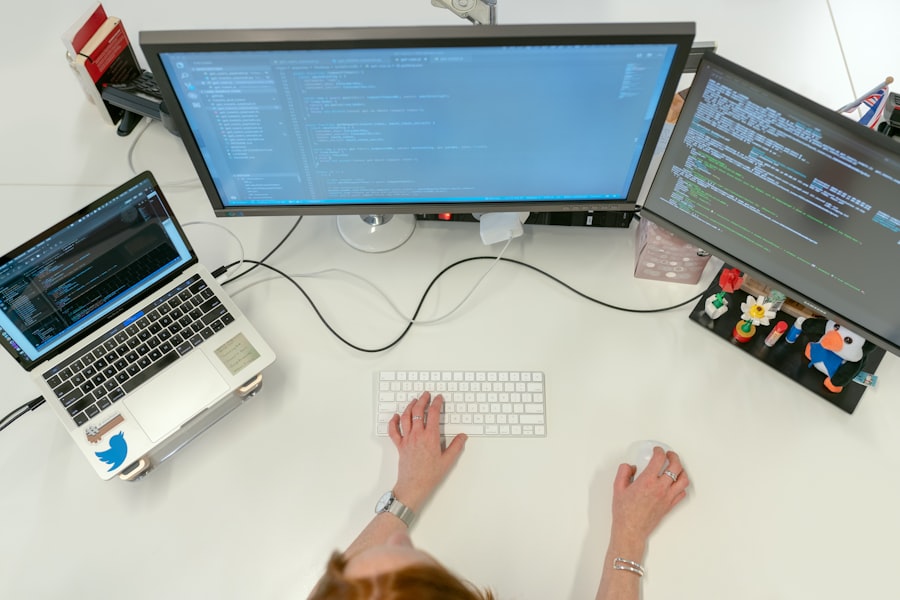

The adoption of EDC software has a profound impact on the speed and efficiency of clinical trials. By digitizing and centralizing data processes, it removes many of the bottlenecks that have historically plagued research.
Accelerating Data Collection and Entry
The direct digital entry of data eliminates the need for manual transcription, a process that is both time-consuming and prone to errors. This can significantly shorten the data collection phase, allowing trials to progress more rapidly. Imagine the time saved by not having to re-enter information from paper forms into a separate database.
Enhancing Data Quality and Integrity
The automated validation rules built into EDC systems are a cornerstone of data quality. By catching errors at the point of entry, these systems prevent flawed data from entering the database. This proactive approach significantly improves data integrity and reduces the need for extensive and costly data cleaning later in the trial. A clean dataset is the bedrock of reliable research findings.
Streamlining Monitoring and Oversight
EDC software provides real-time access to study data, allowing site monitors and data managers to identify trends, deviations, and potential issues much earlier. This enables timely intervention and corrective actions, preventing minor problems from escalating into major ones. This constant visibility is akin to having a bird’s-eye view of the entire operation, allowing for more agile adjustments.
Remote Data Entry and Access
The digital nature of EDC allows authorized personnel to access and manage data remotely. This is particularly beneficial for global trials where data may originate from sites spread across different continents. It facilitates timely review and query resolution regardless of geographical location, acting as a virtual bridge across distances.
Reduced Site Burden
By simplifying data entry and providing clear instructions and validation checks, EDC can reduce the administrative burden on clinical trial sites. This allows site staff to focus more of their attention on patient care and study conduct, rather than on tedious data management tasks.
EDC and Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to regulatory guidelines is paramount in clinical research. EDC software plays a vital role in ensuring compliance with these stringent requirements.
Meeting Good Clinical Practice (GCP) Standards
EDC systems are designed with GCP principles in mind. They facilitate the creation of audit trails that record every action taken on the data, providing a transparent history of data changes. This is essential for regulatory inspections. The system itself acts as a reliable witness, documenting the journey of each piece of data.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Clinical trial data often contains sensitive patient information. EDC software implements robust security measures, including user authentication, access controls, and encryption, to protect data confidentiality and comply with privacy regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. Data security is not an afterthought; it is woven into the fabric of the system.
Audit Trails and Data Traceability
A critical component of regulatory compliance is the ability to trace the origin and any modifications to data. EDC systems maintain comprehensive audit trails, documenting who entered or modified data, when, and why. This level of traceability is essential for demonstrating data integrity to regulatory authorities.
Data Archiving and Retention
EDC solutions typically include features for securely archiving and retaining study data for the periods mandated by regulatory bodies. This ensures that data remains accessible for future reference, analysis, and audits, fulfilling long-term compliance obligations.
Considerations for EDC Implementation
| Metric | Description | Typical Value / Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Entry Speed | Average time taken to input a single patient record | 2-5 minutes per record | High – impacts overall trial efficiency |
| Data Accuracy Rate | Percentage of data entries without errors | 95-99% | Critical – ensures data integrity |
| Query Resolution Time | Average time to resolve data queries raised by monitors | 1-3 days | High – affects data cleaning and trial timelines |
| System Uptime | Percentage of time the EDC system is operational | 99.5% and above | Essential – ensures continuous access |
| Number of Concurrent Users Supported | Maximum users that can access the system simultaneously without performance degradation | 100-1000+ | Important – supports multi-site trials |
| Compliance Standards | Regulatory standards the software adheres to | FDA 21 CFR Part 11, GDPR, HIPAA | Mandatory – for regulatory acceptance |
| Data Export Formats | Supported formats for exporting clinical data | CDISC ODM, CSV, XML | Important – facilitates data analysis |
| Audit Trail Capability | Ability to track all changes made to data entries | Full audit trail with timestamps and user IDs | Critical – ensures data traceability |
While the benefits of EDC are substantial, successful implementation requires careful planning and consideration.
System Selection and Vendor Support
Choosing the right EDC software is a critical decision. Factors to consider include the vendor’s reputation, the software’s scalability, its integration capabilities with other clinical trial systems, and the level of ongoing support provided. A good vendor partnership is like having a skilled co-pilot for a complex journey.
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
When evaluating EDC vendors, it is important to assess their experience in the clinical research field, the robustness of their security protocols, their disaster recovery plans, and the flexibility of their pricing models. Understanding the vendor’s roadmap for future development is also beneficial.
Integration with Other Systems
Seamless integration with other clinical trial management systems (CTMS), safety databases, and laboratory information management systems (LIMS) can further enhance efficiency and data flow. This interconnectedness creates a well-oiled research ecosystem.
Training and User Adoption
Effective user training is essential for successful EDC implementation. Site staff, data managers, and monitors must be adequately trained on how to use the system effectively. High user adoption rates are crucial for realizing the full benefits of EDC. Investing in training is sowing the seeds for future efficiency.
Comprehensive Training Programs
Training should cover all aspects of the EDC system, from basic data entry to advanced query resolution and reporting. Hands-on exercises and real-world scenarios help users gain confidence and proficiency.
Change Management Strategies
Implementing EDC often involves a significant shift in workflow. Effective change management strategies, including clear communication about the benefits of EDC and addressing user concerns, are vital for successful adoption. Overcoming resistance to change is like navigating through turbulent waters; clear communication helps chart a smoother course.
The Future of EDC in Clinical Trials
The evolution of EDC software continues, with ongoing advancements promising even greater efficiencies in clinical research.
Integration with Wearable Devices and IoT
The integration of EDC systems with wearable devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) is paving the way for passive and continuous data collection. This can provide richer, more real-world data with less burden on participants. Imagine collecting vital signs directly from a patient’s smartwatch, eliminating the need for manual input.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are increasingly being explored for applications within EDC, such as predictive analytics for identifying potential data issues, automating certain data review processes, and improving site selection. These technologies have the potential to act as intelligent assistants, augmenting human capabilities.
Predictive Analytics for Data Quality
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential data quality issues before they materialize, allowing for proactive intervention. This is like having an early warning system for data integrity.
Automated Data Review and Cleaning
Machine learning models can be trained to identify and flag anomalies or inconsistencies in data, potentially automating parts of the data review and cleaning process, freeing up human resources for more complex analytical tasks.
Conclusion
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) software has transitioned from a novel technology to an indispensable component of modern clinical trials. By digitizing data management, enhancing data quality, and improving operational efficiency, EDC solutions empower researchers to conduct trials more effectively and bring new treatments to patients faster. Its continued development and integration with emerging technologies promise to further revolutionize the landscape of clinical research, making the process more robust, agile, and ultimately, more successful. The journey of bringing a new medicine to market is long and arduous; EDC software is a sophisticated tool that helps researchers navigate this path with greater precision and speed.