Medical monitoring encompasses a broad spectrum of practices and technologies designed to observe and assess the health status of patients. This field has evolved significantly over the years, driven by advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on patient-centered care. At its core, medical monitoring aims to provide real-time data that can inform clinical decisions, enhance patient safety, and improve health outcomes.
The integration of various monitoring devices, ranging from wearable technology to sophisticated hospital equipment, has transformed how healthcare providers interact with patients and manage their conditions. The significance of medical monitoring extends beyond mere observation; it plays a crucial role in chronic disease management, post-operative care, and preventive health strategies. For instance, patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes or heart disease benefit immensely from continuous monitoring, which allows for timely interventions and adjustments to treatment plans.
Moreover, the data collected through these monitoring systems can be invaluable for research and development, contributing to a deeper understanding of disease progression and treatment efficacy.
Key Takeaways
- Medical monitoring is essential for tracking patient health and treatment efficacy.
- Clinical trials play a critical role in validating new medical monitoring technologies.
- Innovations like wearable devices and AI are transforming medical monitoring capabilities.
- Effective medical monitoring improves patient outcomes and personalized care.
- Regulatory frameworks ensure the safety and reliability of medical monitoring devices.
Importance of Clinical Trials in Medical Monitoring
Clinical trials serve as the backbone of evidence-based medicine, providing the necessary framework to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new medical monitoring technologies. These trials are essential for determining how well a device or system performs in real-world settings, ensuring that it meets the rigorous standards required for clinical use. By involving diverse patient populations, clinical trials can uncover variations in how different demographics respond to monitoring technologies, thereby informing best practices and guidelines.
The importance of clinical trials in medical monitoring is underscored by their role in regulatory approval processes. Before a new monitoring device can be marketed, it must undergo extensive testing to demonstrate its reliability and accuracy. For example, the development of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) involved numerous clinical trials that assessed their performance against traditional blood glucose testing methods.
These trials not only validated the technology but also provided insights into patient adherence and satisfaction, which are critical for successful implementation in everyday clinical practice.
Innovations in Medical Monitoring Technology
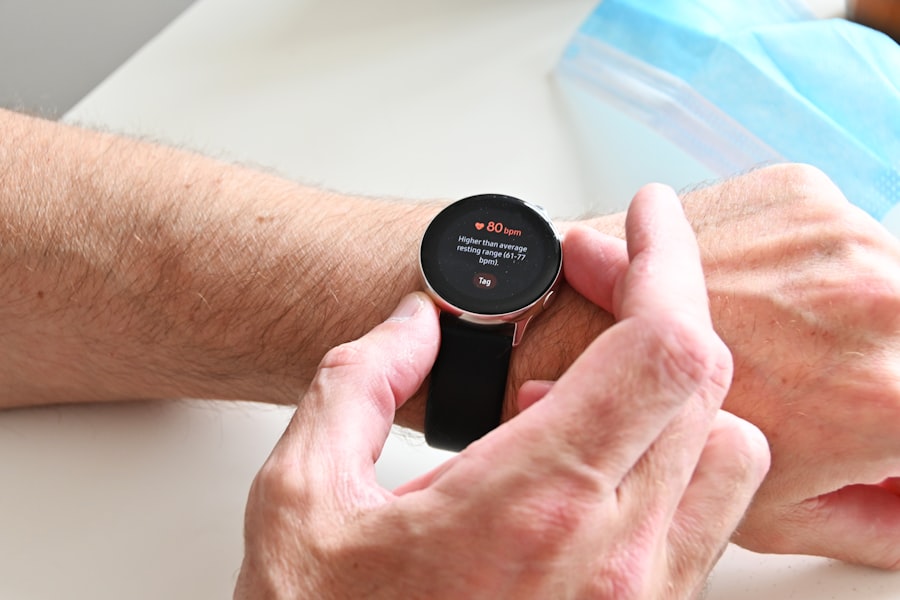
The landscape of medical monitoring technology is rapidly evolving, driven by innovations that enhance the accuracy, accessibility, and usability of monitoring devices. One notable advancement is the rise of wearable health technology, which includes smartwatches and fitness trackers equipped with sensors that monitor vital signs such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, and physical activity levels. These devices empower patients to take an active role in their health management while providing healthcare providers with valuable data that can inform treatment decisions.
Another significant innovation is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into medical monitoring systems. These technologies enable the analysis of vast amounts of data collected from various sources, allowing for predictive analytics that can identify potential health issues before they become critical. For instance, AI-driven algorithms can analyze patterns in heart rate variability to predict cardiac events, enabling timely interventions that could save lives.
The combination of AI with telehealth platforms further enhances remote patient monitoring capabilities, making it easier for healthcare providers to track patients’ health status from afar.
Impact of Medical Monitoring on Patient Care
The impact of medical monitoring on patient care is profound and multifaceted. By providing continuous data on a patient’s health status, monitoring technologies facilitate proactive management of chronic conditions and acute illnesses alike. For example, patients with heart failure can benefit from remote monitoring systems that track weight fluctuations and vital signs, alerting healthcare providers to potential exacerbations before they require hospitalization.
This proactive approach not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces healthcare costs associated with emergency interventions. Moreover, medical monitoring fosters a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare providers. With access to real-time data, patients are more engaged in their care plans and can make informed decisions about their health.
This shift towards shared decision-making is particularly evident in chronic disease management, where patients who actively monitor their conditions often experience better adherence to treatment regimens and improved quality of life. The empowerment that comes from being actively involved in one’s health journey cannot be overstated; it leads to greater satisfaction with care and a stronger commitment to lifestyle changes that promote overall well-being.
Challenges and Opportunities in Medical Monitoring
| Metric | Description | Typical Value/Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Enrollment Rate | Number of patients enrolled per month | 5-20 patients/month | Measures recruitment efficiency |
| Protocol Deviation Rate | Percentage of deviations from the clinical trial protocol | Less than 5% | Ensures data integrity and compliance |
| Adverse Event Reporting Time | Time taken to report adverse events to regulatory bodies | Within 24-48 hours | Critical for patient safety monitoring |
| Data Query Resolution Time | Average time to resolve data queries raised during monitoring | 3-7 days | Ensures data accuracy and completeness |
| Site Monitoring Visit Frequency | Number of monitoring visits per site during the trial | Monthly or quarterly | Maintains site compliance and data quality |
| Source Data Verification (SDV) Percentage | Proportion of data verified against source documents | 20-100% depending on risk-based monitoring | Ensures reliability of collected data |
| Query Rate | Number of data queries per 100 data points | 5-15 queries/100 data points | Indicates data quality and site performance |
| Monitoring Report Submission Time | Time from monitoring visit to report submission | Within 5 business days | Facilitates timely issue resolution |
Despite the numerous benefits associated with medical monitoring, several challenges persist that must be addressed to fully realize its potential. One significant challenge is the issue of data privacy and security. As more patient data is collected through various monitoring devices, concerns about unauthorized access and data breaches have become increasingly prominent.
Healthcare organizations must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive patient information while ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA in the United States. Another challenge lies in the integration of disparate monitoring systems into existing healthcare infrastructures. Many healthcare providers utilize multiple devices and platforms for patient monitoring, leading to fragmented data that can hinder comprehensive patient assessments.
The development of interoperable systems that allow seamless data sharing between devices and electronic health records (EHRs) is essential for creating a holistic view of patient health. This integration presents an opportunity for innovation in health informatics, as developers work towards creating solutions that enhance connectivity and streamline workflows.
Regulatory Considerations for Medical Monitoring Devices

The regulatory landscape for medical monitoring devices is complex and varies significantly across different regions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in overseeing the approval process for new medical technologies. Devices must undergo rigorous testing to demonstrate their safety and effectiveness before they can be marketed to healthcare providers and patients.
This process often involves multiple phases of clinical trials, each designed to address specific questions about the device’s performance. In addition to pre-market approval, ongoing regulatory considerations include post-market surveillance to monitor the long-term safety and effectiveness of devices once they are in use. Manufacturers are required to report adverse events and maintain compliance with quality control standards throughout the product lifecycle.
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, regulatory bodies face the challenge of keeping up with innovations while ensuring patient safety remains paramount. This dynamic environment necessitates collaboration between regulators, manufacturers, and healthcare providers to establish guidelines that foster innovation without compromising safety.
Future Trends in Medical Monitoring
Looking ahead, several trends are poised to shape the future of medical monitoring significantly. One prominent trend is the increasing adoption of personalized medicine, which tailors treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics and preferences. As medical monitoring technologies become more sophisticated, they will enable healthcare providers to gather detailed insights into each patient’s unique health profile, leading to more targeted interventions.
Additionally, the rise of telehealth services has accelerated the demand for remote patient monitoring solutions. As healthcare systems adapt to changing patient needs and preferences, there will be a greater emphasis on developing user-friendly devices that facilitate remote monitoring without compromising accuracy or reliability. The integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) into medical training and patient education also holds promise for enhancing understanding and engagement in health management.
Furthermore, advancements in biotechnology may lead to the development of implantable sensors capable of continuously monitoring various physiological parameters without requiring external devices. These innovations could revolutionize how chronic conditions are managed by providing uninterrupted data streams directly from within the body.
The Role of Clinical Trials in Advancing Medical Monitoring
Clinical trials remain integral to advancing medical monitoring technologies by providing a structured approach to evaluating new devices’ safety and efficacy. Through rigorous testing protocols and diverse participant recruitment strategies, clinical trials ensure that innovations meet the needs of various patient populations while adhering to regulatory standards. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research will be essential for identifying best practices and optimizing the integration of medical monitoring into everyday clinical care.
The future of medical monitoring is bright, characterized by rapid technological advancements that promise to enhance patient care significantly. By leveraging insights gained from clinical trials, healthcare providers can adopt evidence-based practices that improve outcomes while fostering a culture of collaboration between patients and providers. As we move forward into an era where personalized medicine becomes increasingly prevalent, the role of clinical trials will remain pivotal in shaping the landscape of medical monitoring for years to come.




